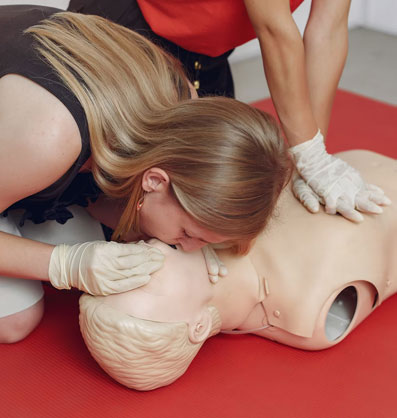
About CPR
CPR stands for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation.
It is a life-saving emergency procedure that is performed when someone's heart stops beating or they stop breathing, such as in cases of cardiac arrest, drowning, or choking.CPR In Simple Terms:
"Cardio" refers to the heart."Pulmonary" refers to the lungs.
"Resuscitation" means reviving someone from unconsciousness or death.
What CPR Does:
Maintains blood flow to the brain and vital organs.Buys time until advanced medical help (like defibrillation or emergency services) arrives.
CPR Includes:
Chest Compressions - Pushing hard and fast in the center of the chest to pump blood.Rescue Breaths (in some cases) - Giving breaths through the mouth to provide oxygen.
When to Perform CPR:
The person is unconscious, not breathing, or not breathing normally (gasping).Call emergency services first, then begin CPR immediately.
Key Facts:
CPR can double or triple a person's chance of survival in a cardiac arrest.Even hands-only CPR (chest compressions without mouth-to-mouth) can be effective.